Understanding Key Health Insurance Terms
Understanding a health insurance policy requires translating insurance industry jargon into plain english. We’ve provided a guide to common insurance terminology and what it really means. (Looking for specific plans & rates? Get info online at SimplyInsured.com)
Understanding Your Deductible
What is a deductible?
Your deductible is the amount of medical bills you have to pay first before your insurance starts to help pay for medical bills. After you’ve spent enough on medical bills to meet the deductible, then you start receiving discounted rates on medical care. There are some medical services where the deductible does not apply, such as preventative care, doctor visits, and prescription drugs.
How does the deductible impact medical premiums and bills?
Insurance plans with lower deductibles tend to have a higher monthly premium, but will start paying for medical bills more quickly. Conversely, insurance plans with higher deductibles tend to have lower monthly premiums, but you will be responsible for more medical bills initially.
Example
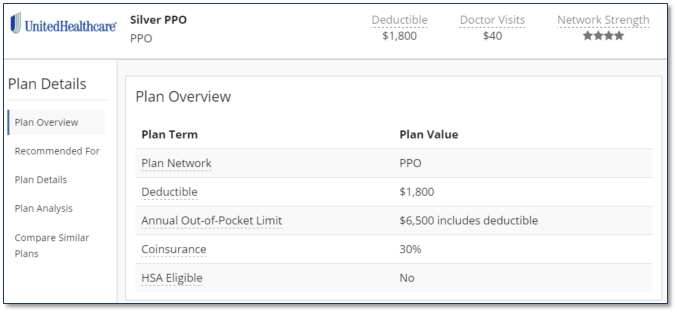
For the above Silver PPO plan, the plan has a deductible of $1800 per year. That means you would be responsible for the first $1800 of medical bills. After you’ve spent $1800, then you start paying a discounted amount for additional medical bills, which in this case is 30% (the co-insurance).
Understanding Your Annual Out-of-Pocket Limit
What is the annual out-of-pocket limit?
The annual out-of-pocket limit (also called the out of pocket maximum) is the most you could end up spending on medical bills in any year. In other words, the out-of-pocket limit is your worst case scenario, you would never be billed for anything above that amount. All insurance plans are legally required to cover all medical bills incurred above the out-of-pocket limit.
How does the annual out-of-pocket limit impact medical premiums and bills?
Insurance plans with a low out-of-pocket limit will cost more in monthly premiums, but can also have a substantial impact on medical bills. A lower out-of-pocket limit can dramatically reduce the amount medical bills paid for major services, such as hospitalization, surgery, labor and delivery, etc., and is one of the most important terms to look at on any plan.
Example

For example, the Silver PPO plan has an out-of-pocket limit of $6500 per year. If you stayed for a week in the hospital stay and get billed $25000 for the hospital stay, your share of the $25000 bill is capped at $6500, and insurance pays for the rest of the bill.
Understanding Your Copay
What is a copay?
A copay is your share of medical bills for a specific service, regardless of the actual cost of that service. Copays are most commonly used on lower cost medical services, such as doctor visits, prescriptions, emergency room visits, and lab tests.
Example
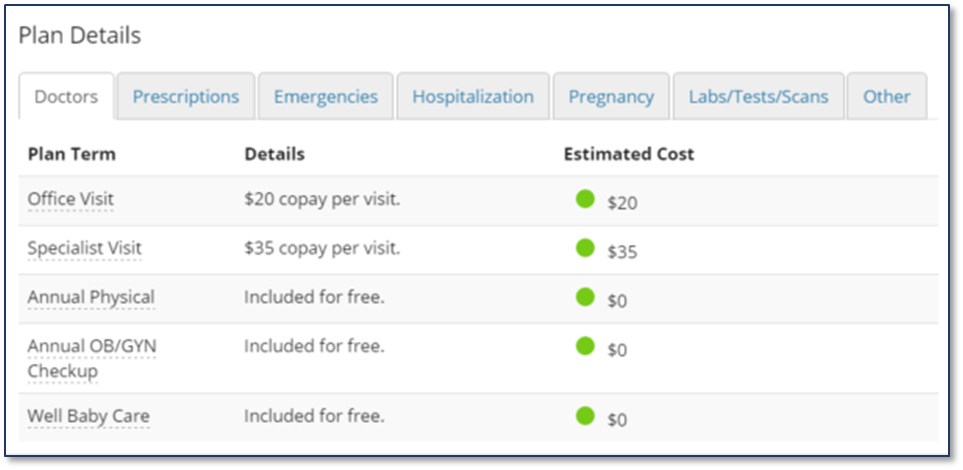
For example, the Silver PPO plan requires you to pay a $20 copay for a standard doctor visit. That would be the only amount you are responsible for out of pocket.
Understanding Your Co-Insurance
What is co-insurance?
Co-insurance is your share of medical bills after your deductible has been met. The co-insurance percentage on a plan is the percentage of costs you pay, and the insurance carrier pays the rest.
Example
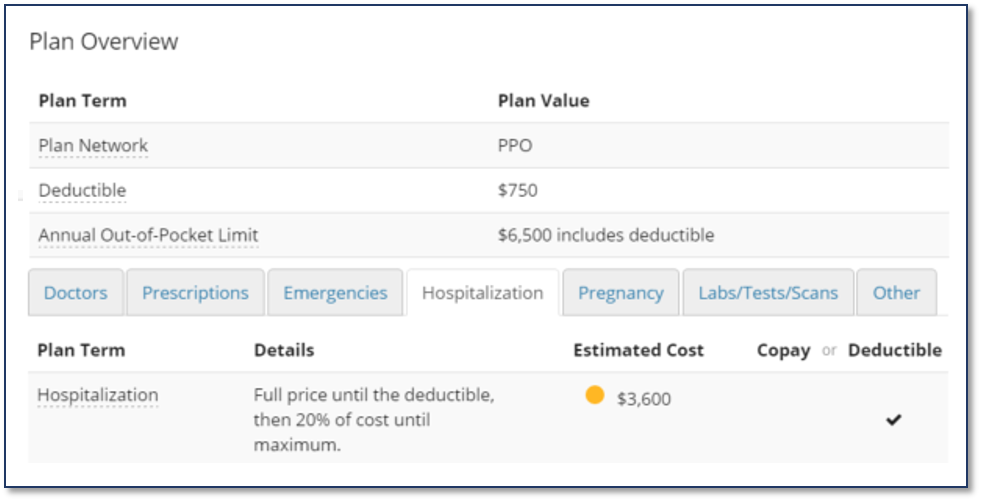
For example, the insurance plan above has a deductible of $750 and 20% co-insurance after the deductible is met. If you incurred a $15000 hospital bill, your share of the bill would be $3600:
- You pay $750 in deductible first
- You then pay 20% of the remaining $14250 bill ($2850)
- Your total out of pocket expense is $3600 ($750+$2850)
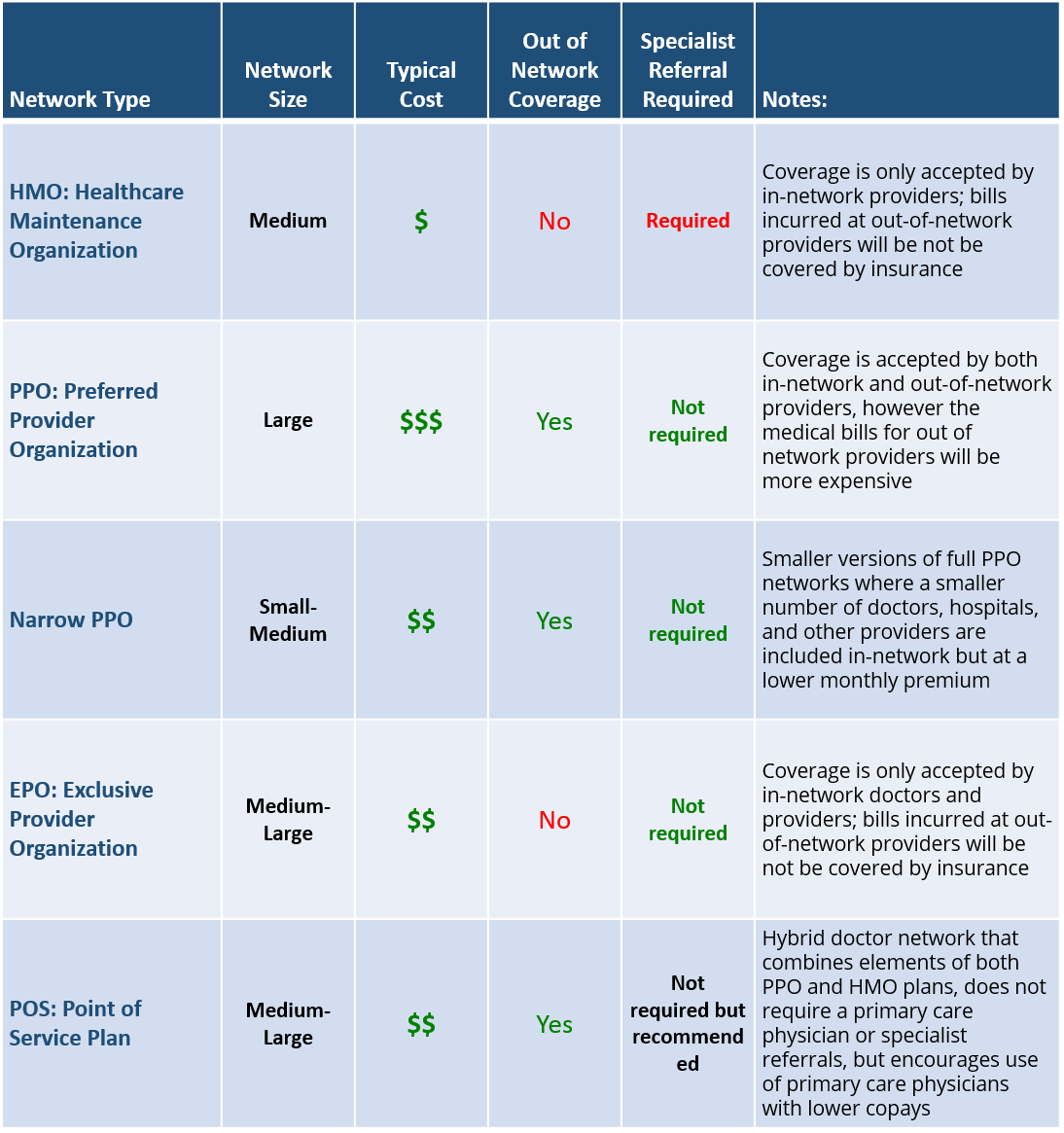
Provider Network
The provider network associated with a health insurance plan impacts 2 important aspects of coverage:
(1) Which doctors, hospitals, and medical providers are in-network with your insurance
(2) Whether your insurance will cover any out-of-network expenses