Introduction
Getting health insurance for your company is an important decision for your company, both for yourself as a business owner and for your employees who will be covering themselves and their families. Making sure that you offer the most appropriate health insurance plan will ensure that your employees are properly covered without overspending on insurance premiums.
Finding the appropriate health insurance plan is easier than you think. This guide will provide you with the tools and knowledge you need to understand health insurance and how to select the appropriate plan for your business.
Guide Contents
- Health Insurance 101 – Understanding what health insurance is and the role is plays for a small business
- Why Small Business Health Insurance – Understand the advantages of offering coverage through your business and how to qualify for group health insurance
- Selecting the Right Plan – How to pick to the right coverage for your business
The Small Business Health Insurance Guide is also available for download here.
Part 1: Health Insurance 101 – how does health insurance work?
When you buy a health insurance plan, you are paying an insurance carrier a monthly fee (the monthly premium) to provide protection when medical bills come up. Having a health insurance plan protects you in 3 ways:
- Access to Quality Medical Care – Health insurance plans provide you with access to a network of doctors, hospitals, pharmacies, and other medical providers who will accept your insurance and provide treatment.
- Reduced Rates on Medical Procedures – Health insurance negotiate discounted rates with medical providers for medical services, and enables you to access services at a lower rate than if you did not have health insurance.
- Protection Against Catastrophic Medical Bills – In a worst case scenario, health insurance plans will cap the amount of medical bills that you personally are responsible for, and pay for 100% of bills that exceed the cap. This protects you from a potential medical bankruptcy when a major medical event occurs.
When comparing health insurance plans, the differences in plans will be mostly around these three dimensions. A more expensive health insurance plan will generally provide:
- Access to a large network of doctors, hospitals, and other medical providers
- Larger discounts on medical procedures
- Lower cap on the amount on medical bills you are responsible for before health insurance pays for 100% of costs
When purchasing a health insurance plan, you will be deciding on whether it makes sense to pay a higher monthly premium in exchange for a larger doctor or lower future medical bills.
What does health insurance cover?
All health insurance plans are legally required to cover any legitimate medical condition. This includes situations as minor as a doctor visit when sick to major events like pregnancy or surgery. The Affordable Care Act also requires all health insurance plan to provide a standard set of benefits called minimum essential coverage.
- Affordability – the plan must cover at least 60% of out of pocket expenses covered medical services
- Can’t be denied for pre-existing conditions – you cannot be denied coverage based on your past health history
- Ten Essential Benefits – medical plans must include coverage 10 core benefits (see below)
- No lifetime dollar limits on coverage – insurance carriers cannot place a lifetime cap on medical bills
Essential Health Benefits
By law, all health insurance plans have to cover the 10 essential health benefits outlined in the Affordable Care Act.
- Preventive Care – Your annual physical, ob-gyn visits, immunizations, any screenings required to keep you healthy, and care for managing a chronic disease such as diabetes and asthma
- Ambulatory Patient Services – Care received outside of the hospital, such as going to a doctor’s office, emergency room, outpatient surgery centers, and home health services
- Emergency Services – Trips to the emergency room and ambulance rides
- Hospitalization – Care you receive in the hospital, including doctors, labs & tests, medication, and room & board. This covers anything that requires inpatient care, such as surgery, labor & delivery, transplants, etc.
- Maternity Care – Care received before and after your baby is born
- Prescription Drugs – Any medications prescribed by a doctor to treat an illness or condition
- Lab Tests – Any testing that helps a doctor diagnose illnesses or injuries or monitor the effectiveness of treatments.
- Mental Health and Substance Abuse Services: Covers both inpatient and outpatient evaluation and treatment of any mental health disorders or substance abuse disorders.
- Rehab Services – Care and equipment to help you recover from injuries, disabilities, or chronic conditions. This includes physical and occupational therapy, speech-language pathology, psychiatric rehabilitation, and more.
- Pediatric Services – Covers dental care and vision care for children under age 19. This includes at least 2 dental cleanings, 1 eye exam, and 1 set of correct lenses.
What does health insurance NOT cover?
While the list of excluded procedures can vary by health insurance companies, there are generally 3 types of services that insurance policies will not cover:
- Cosmetic Surgery
- Weight Loss Programs
- Long Term Care
In addition, there are some procedures that typically are not covered, but occasionally will have limited coverage:
- Infertility Treatments (limited)
- Bariatric Surgery (limited)
- Hearing Aids (limited)
Part 2: Why Small Business Health Insurance Coverage
Advantages of Small Business Health Insurance Coverage
As a small business owner, you have the option of getting coverage either through your business or as an individual through private and government exchanges. The health insurance plans available to small businesses have several advantages over those available to individuals, both in the quality of plans and costs of the plans.
- Tax Deductible Premiums – Health insurance premiums on small business plans are tax deductible for both the company and employees, and reduces the cost of coverage by 25-40%.
- Small Business Tax Credit – Small business with under 25 employees and payroll costs of under $50K per employee potentially qualify for tax credits of up to 50%.
- Larger selection of carriers & plans – There are substantially more plans and carriers available in the small business market (typically 2-3 times as many plans). This provides small businesses with a wider variety of plans in terms of costs and coverage levels.
- Larger doctor networks – most small business plans have larger networks of participation doctors and hospitals compared to individuals plans
How to Qualify for Small Business Health Insurance Coverage
Because of the advantages that a small business plan provides over individual coverage, insurance carriers require that small businesses meet a several requirements to verify their eligibility for small business coverage. Most carriers look at 3 things to determine whether a small business is eligible for small business plans:
- Be registered as a business in your home state
- At least 2 employees working full-time at the company, with one W2 besides the owner
- Payroll history records for salaried employees & tax/ownership documents for owners
In general, most small businesses will easily meet the requirements to be eligible for health insurance coverage.
Eligible Employees for Small Business Health Insurance Coverage
Employees also have to meet a few eligibility requirements in order for them to be covered under a small business health insurance plan. The key eligibility criteria are:
- Works full-time hours. Full-time hours is defined as working 30 hours per week or more. In some states, you are allowed to offer coverage to part-time workers who work as few as 20 hours per week.
- Employed as a W2 employee or owner. In most states, 1099 contractors are not eligible to be covered under the company health insurance plan. There are some exceptions where 1099 contractors are eligible for company coverage if they work full-time hours.
- Satisfied the company probationary period. Companies can choose to require up to a 60 day waiting period before new employees are eligible for insurance coverage.
Part 3: Selecting the Right Plan
Selecting Health Insurance for Your Business and Your Employees
When selecting a health insurance plan for your business and employees, there are 3 questions to ask to better understand what are the most appropriate plans to offer. These questions will help companies to narrow down the hundreds of available policies in the market to the best value plans for your business’ needs.
- What level of coverage do my employees need based on their medical profile?
- What type of doctor network does my employees want?
- How much am I looking to spend on health insurance benefits?
Question 1: What level of coverage do my employees need?
In general, there are 3 broad tiers of coverage available to a small businesses – Bronze, Silver, and Gold/Platinum. Each of these tiers are designed for a specific profile medical needs.
Bronze plans – low cost, high deductible plans for healthy employees
Bronze plans are best suited for healthy employees who have no recurring medical needs, typically only go to their annual check-up, and wants to be protected primarily against major medical events. The reason why the bronze plan works well for this type of person is because:
- Lowest premium cost among all plans, so you aren’t paying extra monthly premiums for coverage the employee won’t utilize
- Provides 100% free preventative care, such as annual physicals, ob-gyn visits, etc
- Caps annual medical bills at $6600 at most if the employee experiences a major medical emergency (e.g. hospitalization, surgery, etc)
- Often are eligible for health savings accounts (HSA), which allow employees to capture tax savings on medical bills
Silver plans – medium cost plans for recurring doctor visits and prescription user
Silver plans are designed for employees who have recurring doctor visits or prescription drug expenses, such as employees with diabetes, asthma, or have recurring doctor/therapy visits. Silver plans offers a low copay on doctor visits and brand name prescription drugs, and will save employees more on their out of pocket medical bills than the higher premium cost of the silver plans. However, the cost of major medical (such as hospitalization) are the same on silver and bronze plans.
- Doctor visits will cost ~$30-50 out of pocket for each visits
- Prescription drugs will cost ~$35-50 for brand name prescription re-fills
- Provides 100% free preventative care, such as annual physicals, ob-gyn visits, etc
- Caps annual medical bills at $6600 at most if the employee experiences a major medical emergency (e.g. hospitalization, surgery, etc)
Gold/Platinum plans – high cost plans with designed to cover major medical events
Gold and platinum plans are the highest cost plans available, and are best suited for employees who anticipate major medical expenses in the next 12 months, such as having a baby, surgery, or hospitalization. Given the high cost of these plans, it would only make sense to offer these plan if employees can save a substantial amount on medical bills.
- Highest premium cost among all plans, so you are paying for lower bills
- Lowest copays on doctor visits and prescriptions
- Caps annual medical bills at around $2000-4000 for major medical emergency (e.g. hospitalization, surgery, etc)
One last thing to keep in mind is that companies are typically allowed to offer multiple plans to employees. So you don’t have to decide on a single plan to fit all of your employees’ health needs, but instead offer plans in each tier and allow employees to select the appropriate coverage level for their own situation.
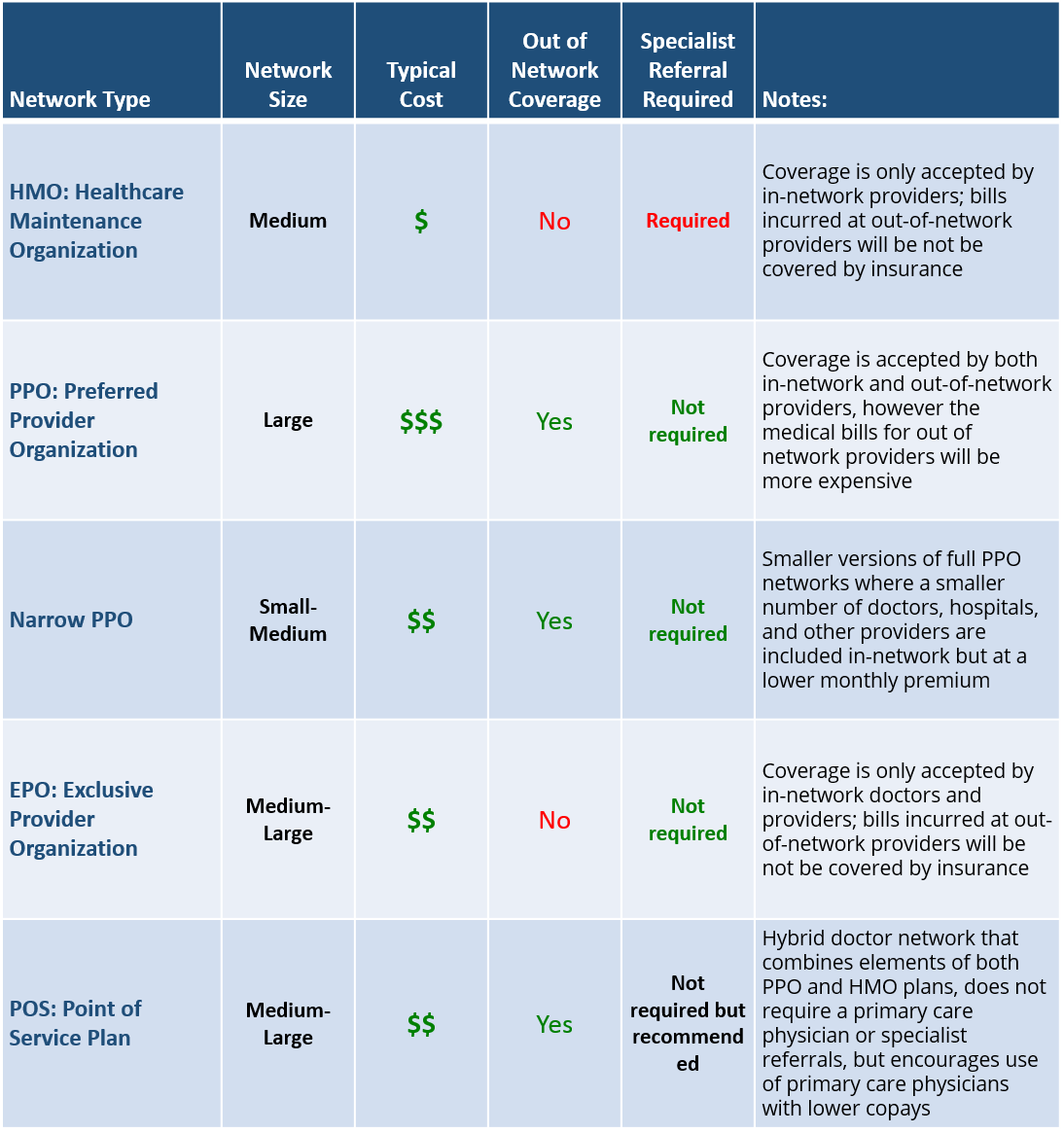
Question 2: What type of doctor network does my employees want?
The type of doctor network available through your insurance plan has a pretty substantial impact on both your monthly premium costs and the availability of doctors and medical providers who will accept the insurance coverage. In general, insurance plans will the largest doctor networks will cost the most in premiums. The primary types of doctor networks are explained below.
Question 3: How much should I spend on health insurance benefits?
You should contribute enough to the cost of the health insurance plans to keep the cost of coverage affordable for employees and provide the appropriate level of coverage for each employee. Companies typically utilize one the following 3 strategies in deciding how much to contribute to the cost of the plans.
Fixed percentage contribution to plan costs – the company will pay for a fixed percentage (e.g. 60%) of each plan’s costs, and the employee pays for the remaining premium.
Paying for base bronze plan – the company will pay for the all or most of a bronze plan’s cost, and then allow employees to pay the difference to upgrade to a higher cost silver or gold/platinum plan
Paying for a silver/gold plan – the company will pay for all or most of a higher tier plan like silver and gold, and allow employees to downgrade to a lower cost plan if they don’t need the higher end coverage. The company then contributes the premium savings to an employee healthcare savings account like a Health Savings Account (HSA) or a Flexible Spending Account (FSA)
Starting a Plan and Getting Your Employees Enrolled
Once you’ve selected a health insurance plan or plans, SimplyInsured provides an easy, online process for getting a plan started. Insurance carriers allow small businesses to begin coverage on the 1st of every month, so there is no need to wait for an open enrollment period to get coverage. Insurance carriers just require applications to be submitted before the 1st of the month to get coverage.
Small businesses are guaranteed to be approved for coverage, and insurance carriers cannot decline coverage to the company or any individual employees for any pre-existing medical conditions.
- The enrollment process consists of 4 steps, all completed online:
- Filling out a company application
- Filling out an enrollment form for each employee
- Uploading proof of payroll
- Making the 1st month premium payment